volcano 的原文地址在 xiaorui.cc, 后面对 volcano 的架构及技术实现原理会持续补充.
volcano controller 的实现
- [volcano scheduler 的实现](#volcano scheduler 的实现)
- [volcano 调度器基本概念](#volcano 调度器基本概念)
- [启动入口 Run](#启动入口 Run)
- [执行调度 runOnce](#执行调度 runOnce)
- [scheduler action 是如何注册的 ?](#scheduler action 是如何注册的 ?)
- [scheduler action 的设计实现](#scheduler action 的设计实现)
- [scheduler 插件的设计实现](#scheduler 插件的设计实现)
- 插件的注册过程
- [gang 插件实现](#gang 插件实现)
volcano scheduler 的实现
volcano 调度器基本概念
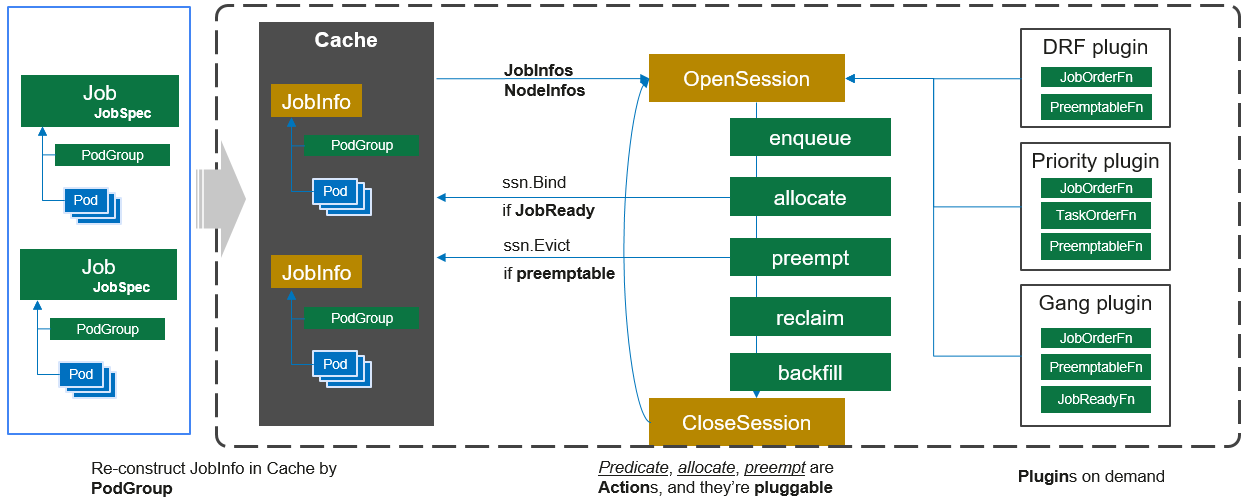
Volcano Schedule r是负责 Pod 调度的组件,它由一系列 action 和 plugin 组成。action 定义了调度各环节中需要执行的动作;plugin 根据不同场景提供了 action 中算法的具体实现细节。Volcano scheduler 具有高度的可扩展性,您可以根据需要实现自己的 action 和plugin。
Volcano scheduler 的工作流程如下:
- 客户端提交的 Job 被 scheduler 观察到并缓存起来。
- 周期性的开启会话,一个调度周期开始。
- 将没有被调度的Job发送到会话的待调度队列中。
- 遍历所有的待调度Job,按照定义的次序依次执行 enqueue、allocate、preempt、reclaim、backfill 等动作,为每个Job找到一个最合适的节点。将该Job 绑定到这个节点。action中执行的具体算法逻辑取决于注册的plugin中各函数的实现。
- 关闭本次会话。
启动入口 Run
// Run runs the Scheduler
func (pc *Scheduler) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
// 加载配置
pc.loadSchedulerConf()
// 监听文件,有变动则变更配置
go pc.watchSchedulerConf(stopCh)
// 启动各个资源的 informer 对象
go pc.cache.Run(stopCh)
// 等待资源 informer 同步完成
pc.cache.WaitForCacheSync(stopCh)
// 执行调度,每秒进行一次调度。
go wait.Until(pc.runOnce, pc.schedulePeriod, stopCh)
}
执行调度 runOnce
func (pc *Scheduler) runOnce() {
klog.V(4).Infof("Start scheduling ...")
scheduleStartTime := time.Now()
defer klog.V(4).Infof("End scheduling ...")
pc.mutex.Lock()
actions := pc.actions
plugins := pc.plugins
configurations := pc.configurations
pc.mutex.Unlock()
// 构建 framework session
ssn := framework.OpenSession(pc.cache, plugins, configurations)
defer framework.CloseSession(ssn)
for _, action := range actions {
// 遍历执行 action
action.Execute(ssn)
}
}
scheduler action 是如何注册的 ?
代码位置: pkg/scheduler/actions/factory.go
注册 action 到 framework action 集合
import (
"volcano.sh/volcano/pkg/scheduler/actions/allocate"
"volcano.sh/volcano/pkg/scheduler/actions/backfill"
"volcano.sh/volcano/pkg/scheduler/actions/elect"
"volcano.sh/volcano/pkg/scheduler/actions/enqueue"
"volcano.sh/volcano/pkg/scheduler/actions/preempt"
"volcano.sh/volcano/pkg/scheduler/actions/reclaim"
"volcano.sh/volcano/pkg/scheduler/actions/reserve"
"volcano.sh/volcano/pkg/scheduler/framework"
)
func init() {
framework.RegisterAction(reclaim.New())
framework.RegisterAction(allocate.New())
framework.RegisterAction(backfill.New())
framework.RegisterAction(preempt.New())
framework.RegisterAction(enqueue.New())
framework.RegisterAction(elect.New())
framework.RegisterAction(reserve.New())
}
注册方法
位置: pkg/scheduler/framework/plugins.go
// Action management
var actionMap = map[string]Action{}
// 把 action 注册进来
func RegisterAction(act Action) {
pluginMutex.Lock()
defer pluginMutex.Unlock()
actionMap[act.Name()] = act
}
// 初始时通过该方法传入 name 获取 action 对象.
func GetAction(name string) (Action, bool) {
pluginMutex.Lock()
defer pluginMutex.Unlock()
act, found := actionMap[name]
return act, found
}
scheduler action 的设计实现
enqueue
Enqueue action 是调度流程中的准备阶段,只有当集群资源满足作业调度的最小资源请求,作业状态才可由 pending 变为 enqueue。
enqueue action 部分
func (enqueue *Action) Execute(ssn *framework.Session) {
queues := util.NewPriorityQueue(ssn.QueueOrderFn)
queueMap := map[api.QueueID]*api.QueueInfo{}
jobsMap := map[api.QueueID]*util.PriorityQueue{}
// 遍历所有不同 queue 的 jobs 集合
for _, job := range ssn.Jobs {
// 迭代的 queue 不存在,则忽略
if queue, found := ssn.Queues[job.Queue]; !found {
continue
} else if _, existed := queueMap[queue.UID]; !existed {
queueMap[queue.UID] = queue
// 把 queue 入队.
queues.Push(queue)
}
// ...
}
for {
// 空则退出
if queues.Empty() {
break
}
queue := queues.Pop().(*api.QueueInfo)
// 获取 queue 对应的 jobs 对象.
jobs, found := jobsMap[queue.UID]
if !found || jobs.Empty() {
continue
}
// 转义为 job 对象
job := jobs.Pop().(*api.JobInfo)
// 当 job 没有配置最小资源限制,或满足 job 所需资源,则更改 job 状态为 inqueue.
if job.PodGroup.Spec.MinResources == nil || ssn.JobEnqueueable(job) {
ssn.JobEnqueued(job)
job.PodGroup.Status.Phase = scheduling.PodGroupInqueue
ssn.Jobs[job.UID] = job
}
}
}
JobEnqueueable 通过调用 enqueue 关联的 plugin 插件判断是否满足资源。
...
allocate
Allocate action 负责通过一系列的预选和优选算法筛选出最适合的节点。
代码位置: pkg/scheduler/actions/allocate/allocate.go
func (alloc *Action) Execute(ssn *framework.Session) {
// ...
// ...
// ...
pendingTasks := map[api.JobID]*util.PriorityQueue{}
// 获取所有未被锁定的 nodes 集合.
allNodes := ssn.NodeList
unlockedNodes := allNodes
if targetJob != nil && len(util.Reservation.LockedNodes) != 0 {
unlockedNodes = unlockedNodes[0:0]
for _, node := range allNodes {
if _, exist := util.Reservation.LockedNodes[node.Name]; !exist {
unlockedNodes = append(unlockedNodes, node)
}
}
}
// 预选函数 ?
predicateFn := func(task *api.TaskInfo, node *api.NodeInfo) error {
// Check for Resource Predicate
if !task.InitResreq.LessEqual(node.FutureIdle(), api.Zero) {
return api.NewFitError(task, node, api.NodeResourceFitFailed)
}
// 进行预选
return ssn.PredicateFn(task, node)
}
// ...
var orderedJobs string
for {
if namespaces.Empty() {
break
}
// pick namespace from namespaces PriorityQueue
namespace := namespaces.Pop().(api.NamespaceName)
queueInNamespace := jobsMap[namespace]
// 获取 queue
var queue *api.QueueInfo
for queueID := range queueInNamespace {
currentQueue := ssn.Queues[queueID]
// 如果当前 queue 过载,则跳过
if ssn.Overused(currentQueue) {
delete(queueInNamespace, queueID)
continue
}
if jobs, found := queueInNamespace[currentQueue.UID]; found && jobs.Empty() {
continue
}
if queue == nil || ssn.QueueOrderFn(currentQueue, queue) {
queue = currentQueue
}
}
if queue == nil {
continue
}
klog.V(3).Infof("Try to allocate resource to Jobs in Namespace <%s> Queue <%v>", namespace, queue.Name)
// 获取 job 对象
job := jobs.Pop().(*api.JobInfo)
var nodes []*api.NodeInfo
// 代码套用了全局变量,乱.
if targetJob != nil && job.UID == targetJob.UID {
klog.V(4).Infof("Try to allocate resource to target job: %s", job.Name)
nodes = allNodes
} else {
nodes = unlockedNodes
}
if _, found = pendingTasks[job.UID]; !found {
tasks := util.NewPriorityQueue(ssn.TaskOrderFn)
for _, task := range job.TaskStatusIndex[api.Pending] {
// Skip BestEffort task in 'allocate' action.
if task.Resreq.IsEmpty() {
klog.V(4).Infof("Task <%v/%v> is BestEffort task, skip it.",
task.Namespace, task.Name)
continue
}
tasks.Push(task)
}
pendingTasks[job.UID] = tasks
}
tasks := pendingTasks[job.UID]
// 尝试为 job 分配资源
stmt := framework.NewStatement(ssn)
for !tasks.Empty() {
task := tasks.Pop().(*api.TaskInfo)
// 节点的预选
predicateNodes, fitErrors := util.PredicateNodes(task, nodes, predicateFn)
if len(predicateNodes) == 0 {
job.NodesFitErrors[task.UID] = fitErrors
break
}
// 找出满足资源的节点
var candidateNodes []*api.NodeInfo
for _, n := range predicateNodes {
if task.InitResreq.LessEqual(n.Idle, api.Zero) || task.InitResreq.LessEqual(n.FutureIdle(), api.Zero) {
candidateNodes = append(candidateNodes, n)
}
}
// 没有合适的节点,直接跳出.
if len(candidateNodes) == 0 {
continue
}
// 把满足资源要求的节点进行优先级打分排序
nodeScores := util.PrioritizeNodes(task, candidateNodes, ssn.BatchNodeOrderFn, ssn.NodeOrderMapFn, ssn.NodeOrderReduceFn)
// 从打分的节点中找到最优的节点
node := ssn.BestNodeFn(task, nodeScores)
if node == nil {
node = util.SelectBestNode(nodeScores)
}
if task.InitResreq.LessEqual(node.Idle, api.Zero) {
klog.V(3).Infof("Binding Task <%v/%v> to node <%v>",
task.Namespace, task.Name, node.Name)
// 进行 node 绑定操作.
if err := stmt.Allocate(task, node); err != nil {
}
} else {
// 如果最优节点不满足资源要求.
if task.InitResreq.LessEqual(node.FutureIdle(), api.Zero) {
stmt.Pipeline(task, node.Name)
}
}
if ssn.JobReady(job) && !tasks.Empty() {
jobs.Push(job)
break
}
}
// 调用 plugin 插件集, 无异常则事务提交.
if ssn.JobReady(job) {
stmt.Commit()
} else {
if !ssn.JobPipelined(job) {
orderedJobs += fmt.Sprintf("%s/%s,", job.Namespace, job.Name)
stmt.Discard()
}
}
namespaces.Push(namespace)
}
if err := updateOrderedJobsInQueue(orderedJobs); err != nil {
}
}
preempt
Preempt action 负责根据优先级规则为同一队列中高优先级任务执行抢占调度。queue 内的不同 job 可以参与抢占,job 内的 task 也可参与抢占。
内部的 plugin 实现细节没看懂 😅
func (alloc *Action) Execute(ssn *framework.Session) {
klog.V(3).Infof("Enter Preempt ...")
defer klog.V(3).Infof("Leaving Preempt ...")
// 记录不同 queue 的 job 优先级
preemptorsMap := map[api.QueueID]*util.PriorityQueue{}
// 记录不同 job 的 task 优先级
preemptorTasks := map[api.JobID]*util.PriorityQueue{}
var underRequest []*api.JobInfo
queues := map[api.QueueID]*api.QueueInfo{}
for _, job := range ssn.Jobs {
// pending 忽略,等待 enqueeu action 标记。
if job.IsPending() {
continue
}
// ...
// 记录所有 queue 对象信息
if queue, found := ssn.Queues[job.Queue]; !found {
continue
} else if _, existed := queues[queue.UID]; !existed {
queues[queue.UID] = queue
}
// 检查job是否正在启动以获取更多资源.
if ssn.JobStarving(job) {
if _, found := preemptorsMap[job.Queue]; !found {
preemptorsMap[job.Queue] = util.NewPriorityQueue(ssn.JobOrderFn)
}
// 把 job 和 task 分别插入不同类型的优先级队列里.
preemptorsMap[job.Queue].Push(job)
underRequest = append(underRequest, job)
preemptorTasks[job.UID] = util.NewPriorityQueue(ssn.TaskOrderFn)
for _, task := range job.TaskStatusIndex[api.Pending] {
preemptorTasks[job.UID].Push(task)
}
}
}
// 在同一个queue的不同 jobs 进行抢占.
for _, queue := range queues {
for {
preemptors := preemptorsMap[queue.UID]
// If no preemptors, no preemption.
if preemptors == nil || preemptors.Empty() {
klog.V(4).Infof("No preemptors in Queue <%s>, break.", queue.Name)
break
}
preemptorJob := preemptors.Pop().(*api.JobInfo)
stmt := framework.NewStatement(ssn)
assigned := false
// 遍历 queue 下的不同 job
for {
// 检查 job 的资源请求情况.
if !ssn.JobStarving(preemptorJob) {
break
}
// job 为空,直接跳出,处理下一个 job.
if preemptorTasks[preemptorJob.UID].Empty() {
break
}
preemptor := preemptorTasks[preemptorJob.UID].Pop().(*api.TaskInfo)
// 进行抢占
if preempted, _ := preempt(ssn, stmt, preemptor, func(task *api.TaskInfo) bool {
// Ignore task with empty resource request.
if task.Resreq.IsEmpty() {
return false
}
// Preempt other jobs within queue
return job.Queue == preemptorJob.Queue && preemptor.Job != task.Job
}); preempted {
assigned = true
}
}
if ssn.JobPipelined(preemptorJob) {
stmt.Commit()
} else {
stmt.Discard()
continue
}
if assigned {
preemptors.Push(preemptorJob)
}
}
// 在同一个 queue 的 jobs 里不同 task 之间进行抢占.
for _, job := range underRequest {
preemptorTasks[job.UID] = util.NewPriorityQueue(ssn.TaskOrderFn)
for _, task := range job.TaskStatusIndex[api.Pending] {
preemptorTasks[job.UID].Push(task)
}
for {
if _, found := preemptorTasks[job.UID]; !found {
break
}
if preemptorTasks[job.UID].Empty() {
break
}
preemptor := preemptorTasks[job.UID].Pop().(*api.TaskInfo)
stmt := framework.NewStatement(ssn)
// 进行抢占.
assigned, _ := preempt(ssn, stmt, preemptor, func(task *api.TaskInfo) bool {
return preemptor.Job == task.Job
})
stmt.Commit()
// 如果没抢占,则进行下一个 job.
if !assigned {
break
}
}
}
}
// call victimTasksFn to evict tasks
victimTasks(ssn)
}
reclaim
Reclaim action 负责当一个新的任务进入待调度队列,但集群资源已不能满足该任务所在队列的要求时,根据队列权重 回收 队列应得资源
每个 queue 按照一定权重把集群物理资源分了。 在应得的资源配额内,随时可以拿到。如果某个队列资源使用超过应得配额,另一个暂时没有要调度的任务,那么可以把这部分没使用的资源拿回来。相当于空闲队列暂时把资源借给别的队列使用,需要的时候会收回来。
代码复杂,还在看。
reclaim
Backfill action 是调度流程中的回填步骤,处理待调度Pod列表中没有指明资源申请量的Pod调度,在对单个Pod执行调度动作的时候,遍历所有的节点,只要节点满足了Pod的调度请求,就将Pod调度到这个节点上。
func (alloc *Action) Execute(ssn *framework.Session) {
for _, job := range ssn.Jobs {
if job.IsPending() {
continue
}
for _, task := range job.TaskStatusIndex[api.Pending] {
if job.IsPending() {
continue
}
// 该任务的 resource request 为空.
if task.InitResreq.IsEmpty() {
allocated := false
fe := api.NewFitErrors()
for _, node := range ssn.Nodes {
// 通过预选插件判断 node 是否满足要求
if err := ssn.PredicateFn(task, node); err != nil {
continue
}
// 尝试绑定 node
if err := ssn.Allocate(task, node); err != nil {
continue
}
allocated = true
break
}
// ...
}
}
}
}
backfill
Backfill action 是调度流程中的回填步骤,处理待调度 Pod 列表中没有指明资源申请量的Pod调度,在对单个Pod执行调度动作的时候,遍历所有的节点,只要节点满足了Pod的调度请求,就将 Pod 调度到这个节点上。
func (alloc *Action) Execute(ssn *framework.Session) {
for _, job := range ssn.Jobs {
// 忽略,等待 enqueue 判断符合资源要求。
if job.IsPending() {
continue
}
if vr := ssn.JobValid(job); vr != nil && !vr.Pass {
continue
}
for _, task := range job.TaskStatusIndex[api.Pending] {
// 如果 task 的 req 未被配置。
if task.InitResreq.IsEmpty() {
allocated := false
fe := api.NewFitErrors()
for _, node := range ssn.Nodes {
// 预选节点
if err := ssn.PredicateFn(task, node); err != nil {
continue
}
// task node 绑定
if err := ssn.Allocate(task, node); err != nil {
continue
}
allocated = true
break
}
if !allocated {
job.NodesFitErrors[task.UID] = fe
}
}
}
}
}
scheduler 插件的设计实现
插件的注册过程
volcano 启动时会自动注册 plugin 到 framework 插件集合中.
func init() {
// Plugins for Jobs
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(drf.PluginName, drf.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(gang.PluginName, gang.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(predicates.PluginName, predicates.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(priority.PluginName, priority.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(nodeorder.PluginName, nodeorder.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(conformance.PluginName, conformance.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(binpack.PluginName, binpack.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(reservation.PluginName, reservation.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(tdm.PluginName, tdm.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(overcommit.PluginName, overcommit.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(sla.PluginName, sla.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(tasktopology.PluginName, tasktopology.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(numaaware.PluginName, numaaware.New)
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(exclusive.PluginName, exclusive.New)
// Plugins for Queues
framework.RegisterPluginBuilder(proportion.PluginName, proportion.New)
}
plugin 调用 RegisterPluginBuilder 方法把 plugin 注册到集合里. 下面为 RegisterPluginBuilder 的实现.
var pluginBuilders = map[string]PluginBuilder{}
// RegisterPluginBuilder register the plugin
func RegisterPluginBuilder(name string, pc PluginBuilder) {
pluginMutex.Lock()
defer pluginMutex.Unlock()
pluginBuilders[name] = pc
}
// GetPluginBuilder get the pluginbuilder by name
func GetPluginBuilder(name string) (PluginBuilder, bool) {
pluginMutex.Lock()
defer pluginMutex.Unlock()
pb, found := pluginBuilders[name]
return pb, found
}
volcano scheduler 在每次调度循环时都会创建 framework session 会话,其内部会实例化一遍所有的 plugin.
代码位置: pkg/scheduler/framework/framework.go
// OpenSession start the session
func OpenSession(cache cache.Cache, tiers []conf.Tier, configurations []conf.Configuration) *Session {
ssn := openSession(cache)
ssn.Tiers = tiers
ssn.Configurations = configurations
for _, tier := range tiers {
for _, plugin := range tier.Plugins {
if pb, found := GetPluginBuilder(plugin.Name); !found {
klog.Errorf("Failed to get plugin %s.", plugin.Name)
} else {
plugin := pb(plugin.Arguments)
ssn.plugins[plugin.Name()] = plugin
onSessionOpenStart := time.Now()
plugin.OnSessionOpen(ssn)
metrics.UpdatePluginDuration(plugin.Name(), metrics.OnSessionOpen, metrics.Duration(onSessionOpenStart))
}
}
}
return ssn
}
gang 插件实现
介绍下 gang 插件的设计,初始化 framework session 时会遍历调用插件的 OnSessionOpen 方法,该方法内部会注册各种的调用链。scheduler 在各个 acion 阶段会调用这些个注册的函数。
代码位置: pkg/scheduler/plugins/gang/gang.go
func (gp *gangPlugin) OnSessionOpen(ssn *framework.Session) {
// 检验是否满足 job.MinAvailable.
validJobFn := func(obj interface{}) *api.ValidateResult {
job, ok := obj.(*api.JobInfo)
// ...
if valid := job.CheckTaskMinAvailable(); !valid {
return &api.ValidateResult{
Pass: false,
Reason: v1beta1.NotEnoughPodsOfTaskReason,
Message: "Not enough valid pods of each task for gang-scheduling",
}
}
// job.MinAvailable 大于可运行的任务数,也就是不满足 MinAvailable,则异常.
vtn := job.ValidTaskNum()
if vtn < job.MinAvailable {
return &api.ValidateResult{
Pass: false,
Reason: v1beta1.NotEnoughPodsReason,
Message: fmt.Sprintf("Not enough valid tasks for gang-scheduling, valid: %d, min: %d",
vtn, job.MinAvailable),
}
}
return nil
}
// 在 jobValid 链条里添加验证方法.
ssn.AddJobValidFn(gp.Name(), validJobFn)
preemptableFn := func(preemptor *api.TaskInfo, preemptees []*api.TaskInfo) ([]*api.TaskInfo, int) {
var victims []*api.TaskInfo
jobOccupiedMap := map[api.JobID]int32{}
for _, preemptee := range preemptees {
job := ssn.Jobs[preemptee.Job]
if _, found := jobOccupiedMap[job.UID]; !found {
jobOccupiedMap[job.UID] = job.ReadyTaskNum()
}
// 大于 job.MinAvailable 则可以被抢占
if jobOccupiedMap[job.UID] > job.MinAvailable {
jobOccupiedMap[job.UID]--
victims = append(victims, preemptee)
}
}
return victims, util.Permit
}
// 加入到 preempt/reclaim 链里面.
ssn.AddReclaimableFn(gp.Name(), preemptableFn)
ssn.AddPreemptableFn(gp.Name(), preemptableFn)
// ...
}
Binpack
插件的目的是尽量把一个节点的计算资源填满,尽量不往空白的节点上调度,这样做的目的是能够尽可能减小节点内的碎片,为更大资源请求的Pod预留足够的资源空间,使集群下空闲资源得到最大化的利用。
具体实现上,binpack调度算法是给可以投递的节点打分,分数越高表示节点的资源利用率越高。binpack算法能够尽可能填满节点,将应用负载靠拢在部分节点,这非常有利于K8S集群节点的自动扩缩容功能。
总之,避免计算资源的碎片化,尽量把节点填满,让较为空闲的节点承载更大的任务。避免大任务因为碎片化,无法拿到整块资源。
func (bp *binpackPlugin) OnSessionOpen(ssn *framework.Session) {
// ...
// 节点打分的方法
nodeOrderFn := func(task *api.TaskInfo, node *api.NodeInfo) (float64, error) {
binPackingScore := BinPackingScore(task, node, bp.weight)
return binPackingScore, nil
}
// 如配置生效,则注册节点打分的函数.
if bp.weight.BinPackingWeight != 0 {
ssn.AddNodeOrderFn(bp.Name(), nodeOrderFn)
}
}
func BinPackingScore(task *api.TaskInfo, node *api.NodeInfo, weight priorityWeight) float64 {
score := 0.0
weightSum := 0
requested := task.Resreq
allocatable := node.Allocatable
used := node.Used
for _, resource := range requested.ResourceNames() {
allocate := allocatable.Get(resource)
// node 当前的资源类型的使用情况.
nodeUsed := used.Get(resource)
// 累加资源
resourceWeight := 0
found := false
switch resource {
case v1.ResourceCPU:
resourceWeight = weight.BinPackingCPU
found = true
case v1.ResourceMemory:
resourceWeight = weight.BinPackingMemory
found = true
default:
resourceWeight, found = weight.BinPackingResources[resource]
}
if !found {
continue
}
resourceScore := ResourceBinPackingScore(request, allocate, nodeUsed, resourceWeight)
// 计算分值和权重
score += resourceScore
weightSum += resourceWeight
}
// mapping the result from [0, weightSum] to [0, 10(MaxPriority)]
// 求分值 score/weightSum
if weightSum > 0 {
score /= float64(weightSum)
}
score *= float64(v1alpha1.MaxNodeScore * int64(weight.BinPackingWeight))
// node 越大分值,越有概率被调度.
return score
}
DRF
DRF 调度插件能够满足更多的作业,不会因为一个胖业务,饿死大批小业务。DRF调度算法能够确保在多种类型资源共存的环境下, 尽可能满足分配的公平原则。
DRF调度算法优先考虑集群中业务的吞吐量,适用单次AI训练、单次大数据计算以及查询等批处理小业务场景。
总之,DRF 不会因为一个胖业务,饿死大批的小业务,让小业务也可以拿到调度。
Proportion
Proportion调度算法是使用queue的概念,用来控制集群总资源的分配比例。每一个queue分配到的集群资源比例是一定的。
举例来说,有3个团队,共享一个集群上的资源池:A团队最多使用总集群的40%,B团队最多使用30%,C团队最多使用30%。如果投递的作业量超过团队最大可用资源,就需要排队。
总之,总资源按照比例分配 queue 的资源
Predicate
Predicate plugin 通过 pod、nodeInfo 作为参数,调用 predicateGPU,根据计算结果对作业进行评估预选。
在 AI 的应用场景下,GPU资源是必需,Predicate plugin 可以快速筛选出来需要GPU的进行集中调度。
Priority
Priority plugin 提供了 job、task 排序的实现,以及计算牺牲作业的函数 preemptableFn。job 的排序根据 priorityClassName,task 的排序依次根据 priorityClassName、createTime、id。
当集群运行了多个 Job,但资源不足,并且每个Job下有不等数量的Pod等待被调度的时候,如果使用 Kubernete s默认调度器,那么最终,具有更多Pod数量的Job将分得更多的集群资源。在这种情况下,volcano-scheduler提供算法支持不同的Job以fair-share的形式共享集群资源。
总之,Priority plugin 能够保证优先级高的优先得到调度。
func (pp *priorityPlugin) OnSessionOpen(ssn *framework.Session) {
// 注册 task 排序方法,值越大优先级越高.
taskOrderFn := func(l interface{}, r interface{}) int {
lv := l.(*api.TaskInfo)
rv := r.(*api.TaskInfo)
if lv.Priority == rv.Priority {
return 0
}
if lv.Priority > rv.Priority {
return -1
}
return 1
}
// 注册 task 排序方法
ssn.AddTaskOrderFn(pp.Name(), taskOrderFn)
// 定义 job 排序方法
jobOrderFn := func(l, r interface{}) int {
lv := l.(*api.JobInfo)
rv := r.(*api.JobInfo)
if lv.Priority > rv.Priority {
return -1
}
if lv.Priority < rv.Priority {
return 1
}
return 0
}
// 注册方法
ssn.AddJobOrderFn(pp.Name(), jobOrderFn)
preemptableFn := func(preemptor *api.TaskInfo, preemptees []*api.TaskInfo) ([]*api.TaskInfo, int) {
// preemptor 抢占者
preemptorJob := ssn.Jobs[preemptor.Job]
var victims []*api.TaskInfo
for _, preemptee := range preemptees {
preempteeJob := ssn.Jobs[preemptee.Job]
if preempteeJob.UID != preemptorJob.UID {
// 抢占同一个 queue 里的不同 jobs
if preempteeJob.Priority >= preemptorJob.Priority { // Preemption between Jobs within Queue
klog.V(4).Infof("Can not preempt task <%v/%v>"+
"because preemptee job has greater or equal job priority (%d) than preemptor (%d)",
preemptee.Namespace, preemptee.Name, preempteeJob.Priority, preemptorJob.Priority)
} else {
victims = append(victims, preemptee)
}
} else {
// 抢占同一个 jobs 内的里的不同 tasks
if preemptee.Priority >= preemptor.Priority {
klog.V(4).Infof("Can not preempt task <%v/%v>"+
"because preemptee task has greater or equal task priority (%d) than preemptor (%d)",
preemptee.Namespace, preemptee.Name, preemptee.Priority, preemptor.Priority)
} else {
victims = append(victims, preemptee)
}
}
}
return victims, util.Permit
}
// 注册抢占方法.
ssn.AddPreemptableFn(pp.Name(), preemptableFn)
}
总结
volcano 社区没以前活跃了,几个月前提交的代码,现在都没有合并。😅